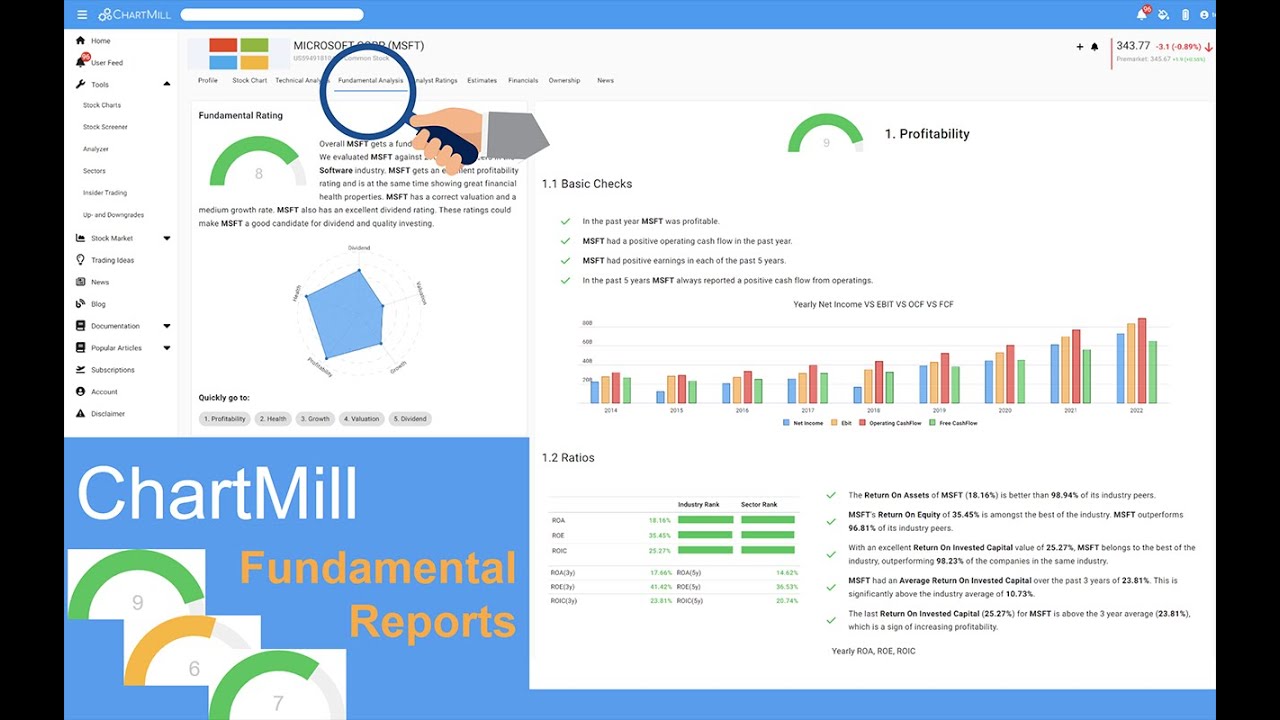
What is Fundamental Analysis?
By Kristoff De Turck - reviewed by Aldwin Keppens
Last update: Apr 19, 2024
FUNDAMENTAL ANALYSIS
Those who mainly rely on fundamental analysis will, when deciding whether or not to buy shares, be led primarily by the company figures. In doing so, both the past, the present and the future are taken into consideration. The fundamental investor's main objective is to value the real intrinsic value of the company. This includes consideration of the answers to the following questions:
- How has the company performed in the past and what is the outlook for the coming years?
- Is the company financially sound?
- How much current debt does the company have and how is it evolving?
- In which market does the company operate and how does the company perform compared to its peers?
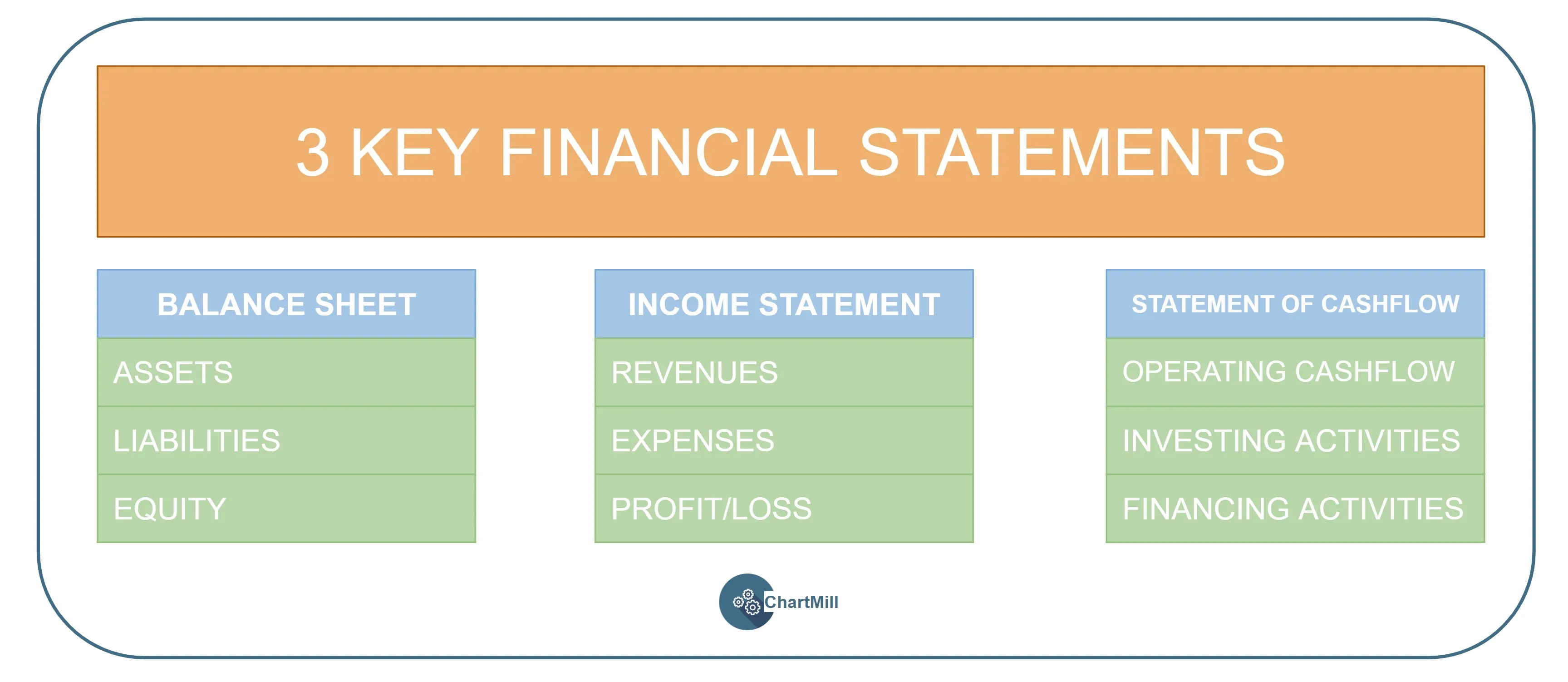
The answers to this can be found in three key financial statements that the company publishes on an annual and/or quarterly basis, being:
The Balance Sheet
The balance sheet provides an overview of the assets, liabilities and equity of an entity (company, institution,...) at a given time.
The Income Statement
The income statement or profit and loss account is a financial statement of a company's revenues, expenses and profits. It gives investors and other interested parties insight into how a business is performing and whether it is capable of producing a profit.
Statement of Cashflows
The Cash Flow Statement shows how much money has flowed into the company and how much money has left the company. Because it is an overview of activities it will always relate to a period just like the Profit and Loss Account. It consists of three types of cash flow, the operating cash flow, the investing cash flow and the financing cash flow
Based on the data in these reports, various ratios are derived which provide a perspective on the overall condition of a company with regard to liquidity, growth, margins, profitability, return on investment, valuation,... etc. Since this analysis is done on the basis of exact figures, it is called the quantitative component of fundamental analysis.
In addition, other general and specific factors may also play an major role if they have an impact on the valuation of a company. Within fundamental analysis, this is the qualitative component where the less tangible issues are addressed. For example:
- Macroeconomic factors (economic growth, business environment, household consumption, ....)
- Management of the firm ( competence and experience of the managers)
- Company's future vision
A good example of an external factor that plays an increasingly important role today is how environmentally and climate-friendly the business processes are and what initiatives have already been taken to minimize the impact. With all this information, the fundamental investor will try to form a picture of the true value that the company represents. If that valuation is above the current price, then the stock is considered worthy of purchase.
Pros and Cons of Fundamental Analysis
Pros
- Fundamental analysis allows you to look ahead based on historical data. Because the analysis is mainly done using published company figures, the analysis is quite objective and rational.
- The nature of the analysis, which is mainly based on (medium) long-term factors, makes this method particularly suitable for those looking to invest for the longer term.
Cons
- fundamental analysis requires a considerable investment of time and it is often difficult for those who are just starting out in investing and have no financial background.
- This form of analysis requires you to analyze not only the company itself. Also a more broad analysis of the competitors, sector colleagues and even industry is necessary if you want to do the analysis thoroughly.
With chartmill, you have the ability to fundamentally screen companies based on many different financial ratios. Learn more about what the terms mean by following this link. (scroll to the bottom of the page).
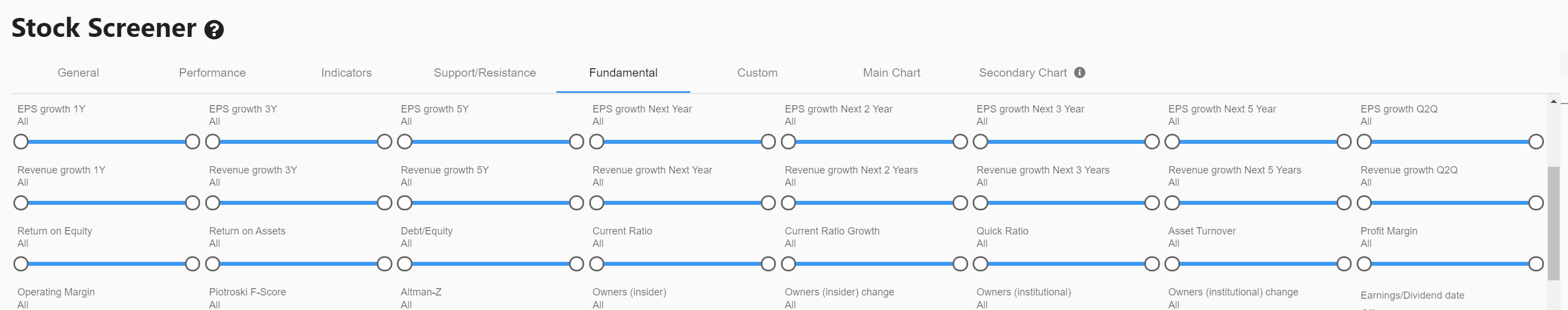
Fundamental analysis is just one method of determining whether or not a company is worthy of purchase. Technical analysis is an alternative way in which a company is valued primarily on the basis of its price movement. In this article you can read more about it (link to be added).
See how the two forms of analysis stand side by side in this summary article.